The Complete Guide to Electric Lamps: Types, Technologies, and Applications

Electric lamps are important in your daily life. They light up your home, streets, and workplaces. Without them, tasks like reading or cooking would be hard. Picking the right lamp affects your comfort and budget. New lights, like LED or Solar Street Lights, use less energy. They save money and help the environment.
Knowing how lamps work helps you choose better. Bright lights are good for work, and soft lights help you relax. Lamps are not just tools—they change how you live and feel around you.
Key Takeaways
Electric lamps come in many types like incandescent, halogen, fluorescent, CFL, LED, and HID. Each type has good and bad points.
LED lamps save the most energy. They use up to 85% less power than older bulbs. They also last longer, saving money on new bulbs.
Picking the right lamp depends on what you need. Bright lights are great for working. Softer lights help you relax.
Smart lamps are easy to use and save energy. You can control them from far away. They can also change based on if you're in the room.
Using energy-saving lamps like LEDs can cut electricity costs. They also help the planet by lowering your carbon footprint.
Types of Electric Lamps

Electric lamps come in different types for various uses. Knowing these types helps you pick the best one for your home, office, or outdoors. Let’s look at three common kinds: incandescent, halogen, and fluorescent lamps.
Incandescent Lamps
Incandescent lights are one of the oldest kinds of lamps. They work by sending electricity through a thin wire, which heats up and glows. These lights give off a warm, cozy glow, perfect for bedrooms or living rooms. But they use a lot of energy. They only give 10 lumens per watt and last about 1,200 hours. This makes them less efficient than newer lights.
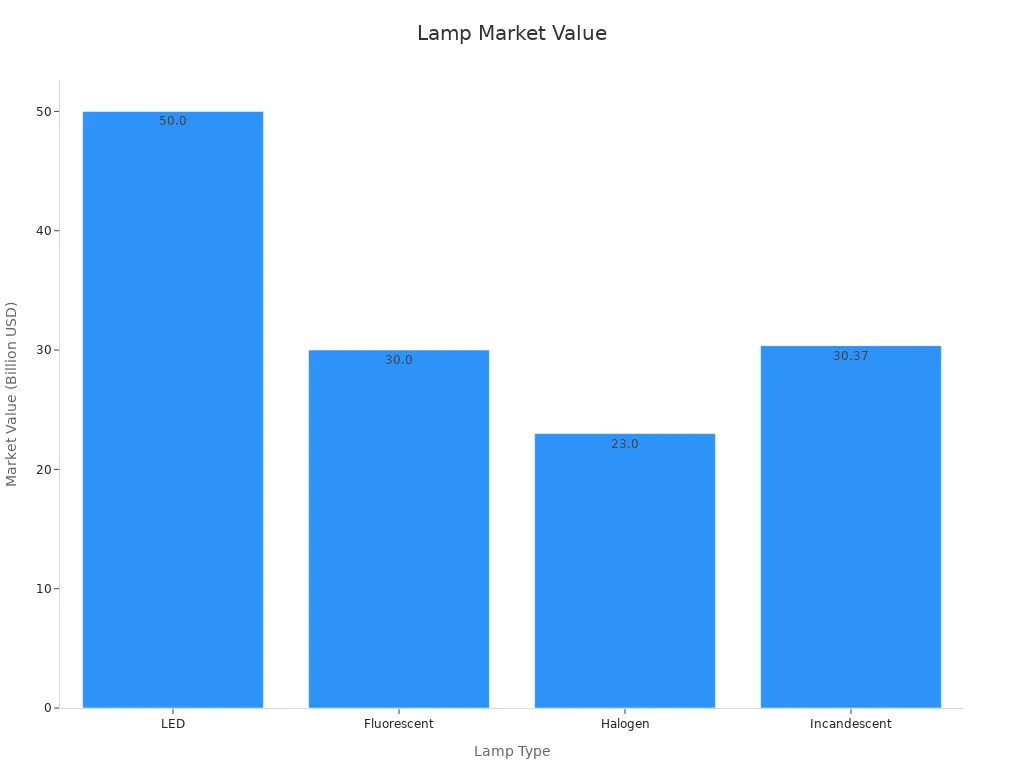
Even though they waste energy, incandescent lamps are still popular. They are cheap and easy to use. In 2023, their market value was $30.37 billion. By 2032, it may grow to $42.12 billion. People still use them for decoration and special lighting.
Halogen Lamps
Halogen lamps are better versions of incandescent lights. They use halogen gas to last longer and work better. These lamps give off bright, white light, great for kitchens or offices. They are more efficient, converting 7–13% of energy into light. They can last up to 10,000 hours, much longer than regular incandescent bulbs.
Halogen lamps are better but not as good as LEDs. In 2023, their market value was $23 billion. It is expected to stay steady as they are used in cars and outdoor lights.
Fluorescent Lamps
Fluorescent lamps are common in offices and factories. They work by sending electricity through a gas-filled tube. This makes ultraviolet light, which hits a coating inside the tube to create visible light. These lamps are very efficient, giving up to 100 lumens per watt. They last 10,000–24,000 hours.
In 2023, the fluorescent lamp market was worth $6.5 billion. It might grow 10% yearly, reaching $7.15 billion by 2030. Businesses like them because they save money and last long. But many are switching to LEDs, which are 44% more efficient, says a University of Michigan study.
Each type of lamp has its own pros and cons. Knowing these can help you choose the right one for your needs.
Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs)
Compact Fluorescent Lamps, or CFLs, are energy-saving bulbs. They use 80% less power than old incandescent bulbs. CFLs also last much longer, about 10,000 hours. This makes them a smart choice for homes and offices.
CFLs work by sending electricity through a gas-filled tube. This creates ultraviolet light, which hits a coating inside the tube. The coating then glows to make visible light. Unlike incandescent bulbs, CFLs don’t heat a wire to glow. This is why they save more energy. However, they take time to fully brighten. They also have a small amount of mercury, so they need careful disposal.
Lamp Type | Energy Savings | Lifespan |
|---|---|---|
Compact Fluorescent | 80% less electricity | Up to 12 times longer |
Incandescent | 100% (baseline) | Typically 1,000 hours |
LED | 75% less electricity | 15,000 to 50,000 hours |
CFLs are great for places where lights stay on for hours. Kitchens and living rooms are good examples. But many people now prefer LED bulbs. LEDs are even more efficient and better for the environment.
LED Lamps
LED lamps are one of the best modern light sources. They use up to 85% less energy than older bulbs. LEDs last a very long time, from 25,000 to 100,000 hours. This means you won’t need to replace them often, saving money and effort.
LEDs work by sending electricity through a special material. This material lights up instantly, unlike CFLs. LEDs also don’t have harmful chemicals like mercury. Most LED bulbs give over 100 lumens per watt. Some advanced ones can even reach 200 lumens per watt. This makes them useful for homes, offices, and factories.
LED technology has improved a lot recently. Many home-use LEDs now give over 100 lumens per watt. The best ones can go beyond 200 lumens per watt.
LEDs come in many colors and styles. They are great for reading, decorating, or outdoor lighting. If you want to save energy and money, switch to LED bulbs.
High-Intensity Discharge (HID) Lamps
High-Intensity Discharge (HID) lamps are very bright and powerful. They are often used outdoors or in big spaces. These lamps create light by making an electric arc in a gas-filled tube. HID lamps are efficient, giving up to 190 lumens per watt.
There are different types of HID lamps, like Metal Halide and High-Pressure Sodium. Metal Halide lamps give bright white light, good for stadiums and parking lots. High-Pressure Sodium lamps give yellowish light, often used for streetlights.
HID lamps give 120 lumens per watt efficiency.
High-Pressure Sodium lamps range from 100 to 190 lumens per watt.
HID lights lose about 70% brightness after 10,000 hours.
HID lamps are strong but have some downsides. They take time to fully brighten and lose efficiency over time. Still, they are a solid choice for lighting large areas.
Smart Lamps
Smart lamps are changing how we light our spaces. These modern lights mix technology with ease of use. They do more than regular bulbs and are part of smart home trends. Smart lamps make life simpler and save energy.
A great feature of smart lamps is phone or system control. You can change brightness, colors, or turn them on remotely. Some even work with voice commands, making them easy to use.
Smart lamps are great for saving energy and controlling light. They adjust brightness based on time or if someone is in the room. For example, they dim at night or turn off when no one is there. This saves power and helps bulbs last longer. The table below shows key benefits of smart lighting:
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Automation and Control | Lights adjust automatically for indoor and outdoor needs. |
Health Benefits | Daylight-like light cuts eyestrain by 84% and drowsiness by 10%. |
Market Growth | |
Data-Driven Insights | Sensors change light based on room use. |
Smart bulbs also make you more comfortable. They copy natural daylight, helping your eyes and focus. This makes them great for studying or working. They also connect with other smart devices for easy home control.
If you want modern, energy-saving lights, smart lamps are a great pick. They are the future of lighting, blending usefulness with eco-friendliness.
Technologies Behind Electric Lamps
How Incandescent Lamps Work
Incandescent lamps are simple and easy to understand. They make light using heat, called thermal radiation. Electricity flows through a thin tungsten wire inside the bulb. The wire heats up because of resistance. This heat makes the wire's atoms excited. When the atoms calm down, they release energy as light. But most energy (about 90%) turns into heat, not light. This makes these lamps wasteful compared to newer ones.
Metric | Value |
|---|---|
Less than 5% | |
16 | |
Comparison with CFL | 60 lm/W |
Comparison with LED | 100 lm/W |
Incandescent bulbs are cheap and give a warm glow. But they don’t last long, only about 1,000 hours. They also use a lot of energy, so they aren’t good for saving money or power.
How Halogen Lamps Work
Halogen lamps are better versions of incandescent bulbs. They also use a tungsten wire, but the bulb has special gases like iodine or bromine. These gases create a halogen cycle. This cycle puts evaporated tungsten back on the wire. It helps the wire last longer and keeps the bulb clear for steady light.
Halogen lamps get hotter than regular incandescent bulbs. This makes them brighter and more efficient. They give off white light, which is great for kitchens or offices. But they still use more energy than LEDs or CFLs. Their bright light makes them good for tasks that need focus.
How Fluorescent and CFLs Work
Fluorescent and CFL bulbs work differently from incandescent ones. Inside the bulb, electricity excites a gas mix, often mercury and argon. This creates ultraviolet (UV) light, which we can’t see. A special coating inside the bulb changes UV light into visible light.
Fluorescent lights are very efficient, giving up to 100 lumens per watt. They last much longer than incandescent bulbs, from 10,000 to 24,000 hours. CFLs are smaller versions of fluorescent lights, made for homes. Both types save energy but have a little mercury, so they need careful disposal.
Fluorescent lights became popular in 1938 for saving energy.
Modern CFLs use less mercury than older ones.
Special coatings improve light quality for homes and offices.
Fluorescent and CFL bulbs are great for saving energy and lasting long. But many people now choose LEDs because they work better and are safer for the planet.
How LED Lamps Work
LED lamps are very efficient and last a long time. They use a process called electroluminescence to make light. Electricity passes through a special material, creating visible light. Unlike old bulbs, LEDs turn most energy into light, not heat. This makes them highly efficient.
Here are some important facts about LED lamps:
Energy Conversion: LEDs give 80-100 lumens per watt. This is much better than incandescent bulbs (10-20 lm/W) and fluorescent lights (35-60 lm/W).
Heat Management: LEDs stay cool, which helps them last longer and reduces cooling costs.
Longevity: These lights can work for tens of thousands of hours, saving money over time.
LEDs come in many colors, shapes, and brightness levels. They are great for homes, offices, and outdoor spaces. Many LEDs also work with smart technology, making them even more useful. If you want eco-friendly and energy-saving lights, LEDs are a great choice.
How HID Lamps Work
HID lamps are used for bright lighting in big areas like stadiums or streets. They create light by making an electric arc inside a gas-filled tube. This arc excites the gas, producing strong light. HID lamps are very bright and efficient, perfect for large spaces.
There are different types of HID lamps, like Metal Halide and High-Pressure Sodium. Metal Halide lamps give white light, while High-Pressure Sodium lamps give yellow light. Some High-Pressure Sodium lamps can last up to 10,000 hours, with 90% still working after that time. Replacing these lamps costs only 5% of the total five-year expense.
HID lamps can reach up to 190 lumens per watt, making them efficient. But they take time to fully brighten and lose efficiency over time. Even with these issues, they are still a good choice for lighting large areas.
Comparing Energy Efficiency Across Lamp Technologies
When looking at energy efficiency, LEDs are the best option. The table below shows how different lamps compare:
Lamp Type | Efficacy (lm/W) |
|---|---|
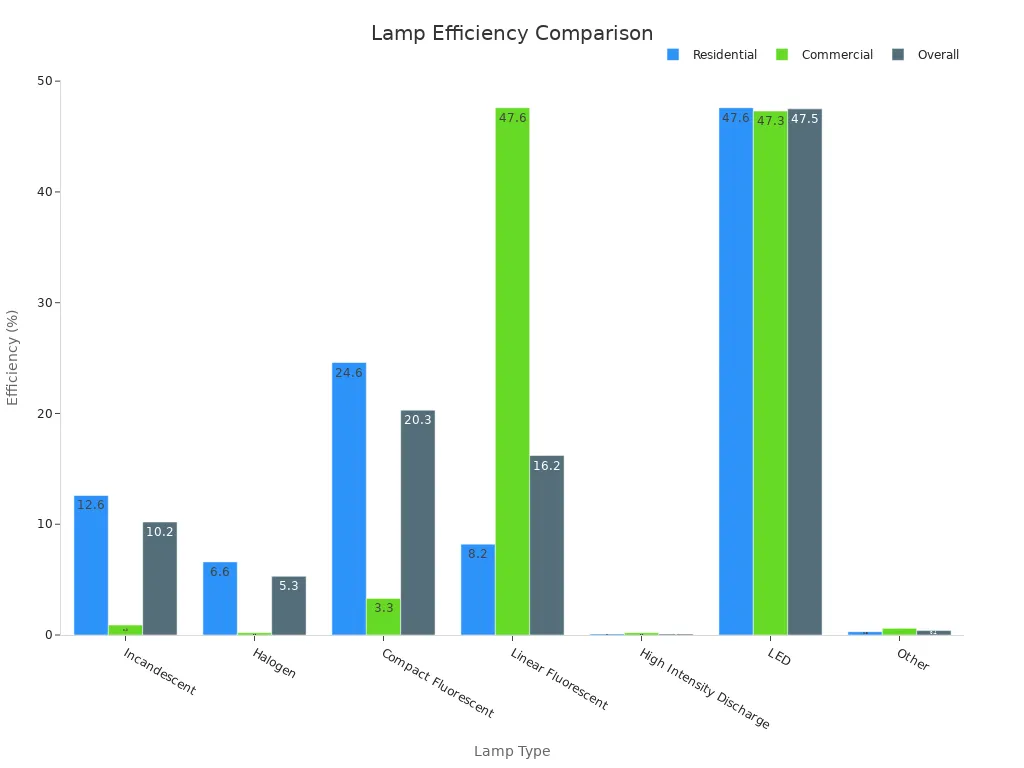
Incandescent | 8 - 22 |
Mercury | 22 - 58 |
Fluorescent | 30 - 38 |
Metal Halide | 74 - 132 |
High Pressure Sodium | 74 - 132 |
Low Pressure Sodium | 70 - 152 |
LED | 10 - 200 |
Incandescent bulbs waste most energy as heat. Fluorescent and CFL lamps are better but not as good as LEDs. HID lamps, like High-Pressure Sodium, are efficient for big spaces. LEDs, however, are the most efficient, reaching up to 200 lumens per watt. They are the best for saving energy and helping the environment.
💡 Tip: Use LED lamps to save money and energy. They are durable, efficient, and work well for all lighting needs.
Applications of Electric Lamps

Electric lamps are used in many places to make life easier. They improve how spaces look and feel. Let’s see how they are used at home, work, and outdoors.
Residential Lighting
At home, lamps help with tasks like reading or cooking. They also create a cozy or calm mood. LED lamps are popular because they save energy and last long. They give bright light but use less power than old bulbs.
Studies show motion sensors with LED lamps save energy. For example, stairwells used 40% less power with these lights. Another study found 57% energy savings in building hallways with adjustable LED lights. These examples show how homes can save energy with smart lighting.
More people now use energy-saving lamps. In 2009, 58% of homes used them. By 2015, this grew to 86%, and 18% of homes stopped using old bulbs. LED lamp use jumped from 4% in 2015 to 47% in 2020.
Commercial and Industrial Lighting
In offices and factories, good lighting helps people work safely and better. Big spaces need strong, efficient lights. LED lamps are the top choice here. They are bright, save energy, and last longer, cutting repair costs.
A report showed LED lamps make up 47.5% of industrial lights. Even though businesses use only 20% of all lights, they use 69% of lighting electricity. This shows why switching to LED lamps is important to save money and energy.
Outdoor and Street Lighting
Outdoor lights keep streets and public areas safe. Streetlights, parking lots, and stadiums often use HID lamps or LEDs. LED lamps are better because they last long and save energy.
Switching to LED streetlights saves a lot of money. New York City replaced 250,000 streetlights with LEDs, saving $6 million yearly on energy and $8 million on repairs. Manchester, New Hampshire, saves $500,000 yearly by using 9,000 LED streetlights. The University of California, Davis, cut outdoor lighting energy by 86%, saving $1.4 million over 15 years.
💡 Tip: Use LED lamps for outdoor areas. They are bright, save energy, and lower repair costs.
Electric lamps have changed how we light homes, workplaces, and public areas. Picking the right lamp can save energy, cut costs, and improve spaces.
Specialty Lighting Uses
Specialty lighting is for tasks beyond regular lighting. It helps with displays, growing plants, and creating special effects. Different lamps are made for specific jobs in various places.
Display and Accent Lighting
Display lighting makes items stand out in stores or museums. Spotlights and track lights are often used for this. They focus light on art, products, or building details. LED lamps work well because they save energy and show bright colors. They can also make spaces feel cozy with soft lighting.
Plant Growth Lighting
Plant lighting helps plants grow indoors or in greenhouses. High-Pressure Sodium (HPS) and LED lamps are popular choices. HPS lamps give strong light but focus it in small areas. LED lamps spread light better and stay cooler, which is good for controlled spaces. Below is a table comparing HPS and LED lamps for plant growth:
Feature | HPS Lamps (1 kW) | LED Lamps (1 kW) |
|---|---|---|
Cost to Buy | $200–$350 per kW | $1000–$3000 per kW |
Light Output Cost | 5–9 µmol/s per dollar | 0.5–1.5 µmol/s per dollar |
Energy Savings | Lower over time | Higher upfront, better later |
Efficiency | At least 1.9 µmol/J | At least 1.9 µmol/J |
Durability | Varies | Needs extra protection |
Heat Levels | Needs high placement | Can be placed lower |
Light Spread | Focused beam | Wider beam |
LED lamps are becoming more popular for growing plants because they save energy and work well in different setups.
Medical and Science Lighting
Medical lamps are important for surgeries and lab work. Surgical lights are bright and don’t cast shadows, helping doctors see clearly. UV lamps kill germs in hospitals and labs, keeping spaces clean and safe.
Stage and Show Lighting
Stage lighting makes shows exciting with cool effects. Spotlights, floodlights, and colored LED lights are used in theaters and concerts. These lights set the mood and highlight key parts of performances.
Specialty lighting shows how lamps do more than just light up rooms. Picking the right lamp for each job helps you get the best results.
Choosing the Right Lamp
Key Factors to Consider
Picking the right lamp depends on a few things. First, think about what you need the light for. Bright lights are good for reading or working. Softer lights are better for relaxing. Next, check the size of the room. Big rooms need stronger lights, while small spaces can use smaller ones.
Energy use is also important. Choose lamps that save energy to lower your bills. The power factor shows how well a lamp uses electricity. A power factor close to 1.0 means it works efficiently. Also, look at how long the lamp lasts. Longer-lasting lamps save money and time since you replace them less often.
Lastly, think about the environment. Energy-saving lamps like LEDs use less power and cut carbon pollution. Studies show LED lamps pay for themselves in just over a year. They also release much less CO2 than high-pressure sodium (HPS) lamps.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Using energy-saving lights helps cut costs and save resources. LED lamps are the best choice for saving energy. They turn 80% of energy into light, while old bulbs only use 10%. A study from the University of Michigan says LEDs are 44% more efficient than fluorescent lights.
Switching to energy-saving lamps can save a lot of money. For example, replacing old lights with LEDs can cut energy bills nearly in half. The table below compares LED and HPS lamps:
Lamp Type | Energy Savings | Cost Reduction | Payback Period | Environmental Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
LED | High | Big Savings | Less CO2 emissions | |
HPS | Moderate | Smaller Savings | Longer | More CO2 emissions |
Choosing energy-efficient lamps saves money and helps the planet.
Durability and Maintenance
Durability and upkeep are important when picking a lamp. Strong lamps last longer, so you don’t need to replace them often. LED lamps can last up to 50,000 hours, much longer than old bulbs. This makes them a smart choice over time.
Different lamps need different care. Old bulbs burn out quickly and need replacing often. LEDs need little care, while HID lamps may dim over time and need fixing. Keeping track of energy use can help plan maintenance and keep lights working well.
Choosing strong, low-maintenance lamps saves time and money. It also keeps your space well-lit for longer.
Choosing the Right Lamp for Your Needs
Picking the right lamp can save energy and money. It also makes your space look and feel better. Different lamps work best for different jobs. Knowing their features helps you choose wisely.
Home Lighting
At home, lights should feel cozy and welcoming. LED bulbs are a great option. They are bright, save energy, and last longer than old bulbs. Use soft LED lights in bedrooms or living rooms to relax. In kitchens or study areas, brighter LEDs help you see and focus better.
Work and Factory Lighting
Offices and factories need strong, steady lights. LED lamps are the best choice because they last long and save energy. They also lower repair costs. For example, a transit company in Pennsylvania saved 64% energy by switching to efficient lights. This cut over 5 million kilowatt-hours of power use each year.
Outdoor and Special Lighting
Outdoor spaces like streets and stadiums need bright lights. HID lamps are often used, but LEDs are now more popular. LEDs save energy and last longer. For special uses, like plant growing or displays, pick lamps that fit the job. LEDs are great for displays because they show colors well and stay cool. For plants, LEDs spread light evenly and don’t get too hot.
The table below shows how matching lamps to tasks can bring big benefits:
Use Case | Energy Saved (%) | KWH Saved | Yearly Maintenance Savings ($) | CO2 Reduced (lbs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
The Franklin Institute | 66% | 264,902 | 7,674 | 896,935 |
Southeastern Pennsylvania Transit Authority | 64% | 5,281,404 | 617,624 | 7,218,366 |
M&T Bank | 61% | 299,598 | 22,691 | 846,554 |
Choosing the right lamp saves energy, cuts costs, and helps the planet. Whether for homes, work, or outdoors, the right lamp makes a big difference.
Learning about electric lamps helps you pick the right ones. Newer lights, like LEDs, have many advantages. They use 90% less energy than old bulbs and last longer. This means you save money over time. Many LED lights also work with smart systems, making them easier to use. These features cut electricity costs and help the planet by using less energy.
Switching to modern lights makes life better. Bright lights are great for working, while soft ones help you relax. Energy-saving lamps give you comfort and help protect the environment too.
FAQ
What is the most energy-efficient type of electric lamp?
LED lamps save the most energy. They turn 85% of energy into light. They also last much longer than other lamps. This helps save money and lower electricity use.
How do I choose the right lamp for my home?
Think about what you need. Bright lights are good for reading or cooking. Softer lights are better for relaxing. LED lamps are a smart pick. They save energy and last a long time.
Are smart lamps worth the investment?
Yes, smart lamps are useful and save energy. You can control them with your phone, change brightness, or set timers. Over time, they cut electricity costs and make lighting easier.
Do fluorescent lamps contain harmful materials?
Yes, fluorescent lamps have a little mercury inside. Be careful when handling them. Dispose of them properly at recycling centers to avoid harming the environment.
Can LED lamps be used outdoors?
Yes, LED lamps are great for outdoor use. They are strong, save energy, and give bright light. Many outdoor LEDs are weatherproof, so they work well in gardens, streets, or parking lots.
💡 Tip: Always check the lamp's details to make sure it fits your needs, indoors or outdoors.
See Also
Exploring Street Light Bulbs: Varieties, Innovations, and Uses
Understanding LED Light Bulbs: Advantages, Features, and Choosing
All You Need to Know About LED Light Bulbs
Industrial LED Bulbs: Performance, Uses, and Choosing Wisely
GE LED Bulbs: Characteristics, Advantages, and How to Choose

