Understanding Halide Lights: How They Work and Their Role in HID Lighting Systems

You might see how Halide Lights change a room’s look in your home. These lights use special gases to create a bright, white light that is perfect for various settings. You can see this light in stores, hospitals, and art galleries, where true color is essential. Halide Lights are special because they provide ample illumination with less power, which means you save money on energy and bulbs. They also have a long lifespan before needing replacement. If you want to learn more About Us and discover how our products can enhance your home or showcase your products, Halide Lights demonstrate how innovative lighting can make a difference.
Key Takeaways
Halide Lights make bright, white light with special gases. This makes them good for stores and stadiums. These lights last a long time. They work for 10,000 to 20,000 hours. This means you do not need to change them often. Halide Lights save energy and give strong light. But they do not save as much energy as LED lights. It is important to recycle halide lights the right way. They have mercury, which can hurt the environment. Halide Lights are still used when true color and strong light are needed. Many people pick them even though LED lights are popular now.
Halide Lights Overview

Definition and Components
Halide Lights shine with a bright, white light. They are part of the HID lamp group. Metal halide lamps are the most used type. Inside each lamp is a small tube. This tube holds mercury vapor, metal halide salts, and tungsten electrodes.
The tungsten electrodes help start the lamp. They make an electric arc. Mercury vapor makes the first light flash. It also keeps the lamp glowing. Metal halide salts can be iodides, bromides, or chlorides. These salts change the color and make the lamp work better. All these parts work together. They help Halide Lights stay strong and last long.
Tip: Metal halide lamps are special. They use both mercury and metal halide salts. Other HID lamps do not use both.
Here is a table that shows how metal halide lamps compare to another common HID lamp:
Feature | Metal Halide | High Pressure Sodium |
|---|---|---|
Light Color | White | Amber Orange |
Ballast Compatibility | Needs a certain ballast | Needs a certain ballast |
Best Applications | Stadiums, construction sites | Not specified |
Warm-up Time | Longest of all light types | Not specified |
Role in HID Systems
Halide Lights are important in HID systems. These systems send electricity through gases in the lamp. This makes plasma inside the lamp. Plasma gives off ultraviolet light. The lamp’s coating changes this to visible light. The light is very bright. It is much stronger than regular bulbs.
Halide Lights work well where you need strong light. They give high luminous efficacy. This means they make lots of light for each watt. They last over 20,000 hours. You do not need to change them often. Their white light and good color make them great for stadiums and factories.
Note: Halide Lights give bright light and true color. This is important for many jobs.
Operation
Electric Arc Process
If you look inside a Halide Light, you can see how it works. When you turn on the lamp, electricity goes into the arc tube. The gases inside start to heat up and turn into vapor. These gases also become charged, or ionized. The ionized gases make an electric arc. This arc is what makes the lamp glow.
Here is how the process works, step by step:
The lamp starts with a warm-up time. The arc tube gets hot.
The halide gases turn into vapor during this time.
A special starter sends a strong electric pulse. This helps the arc start fast and well.
The electric arc forms between the tungsten electrodes. This arc makes the lamp shine.
Tip: The halides inside the lamp help change the color of the light. You can adjust the color by using different halide salts.
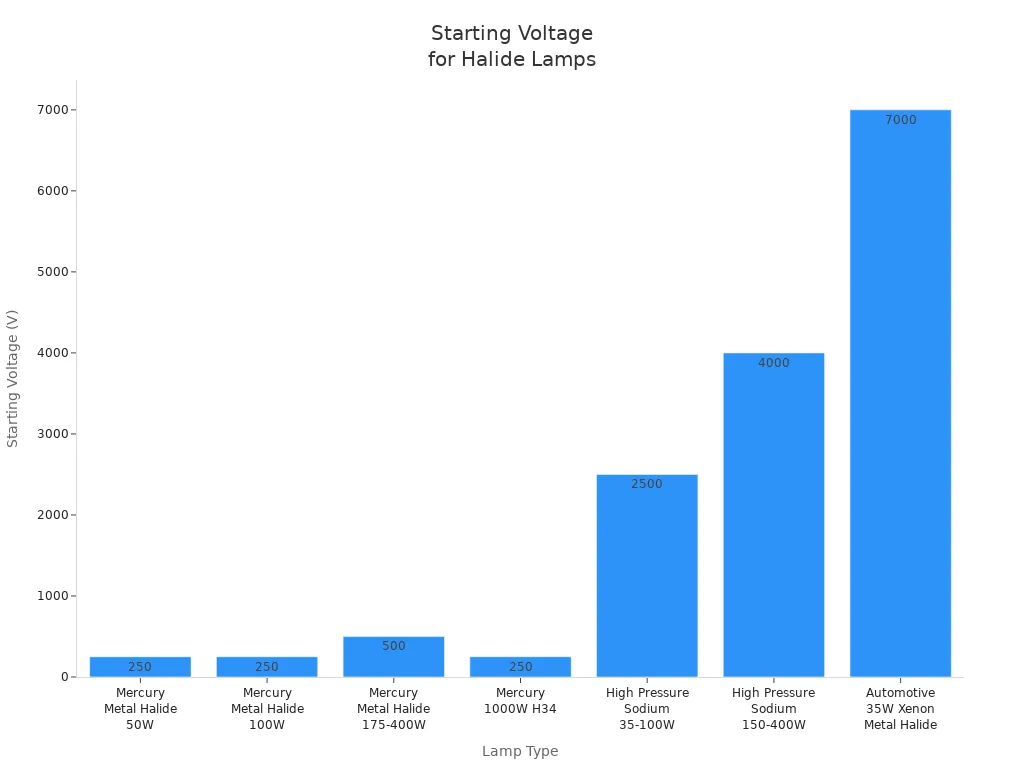
The voltage and current needed to start and run these lamps can be different. You can see the differences in the table below:
Lamp Type | Normal Arc Voltage (V) | Minimum Voltage (V) | Starting Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|---|
Mercury and Metal Halide 50 watt | 95 | 11 | 250 |
Mercury and Metal Halide 100 watt | 115 | 12 | 250 |
Mercury and Metal Halide 175-400 watt | 135-140 | 13 | 500 |
Mercury 1000 watt H34 | 135-140 | 14 | 250 |
High Pressure Sodium 35-100 watts | 55 | 11-13 | 2500 |
High Pressure Sodium 150-400 watts | 100 | 12-15 | 4000 |
Automotive 35W Xenon Metal Halide | 80-90 | 20's | 7000-20000 |
Color Profile and Quality
Halide Lights give off a bright, white color. The color temperature can go as high as 5500K. This makes the light look like sunlight. The color rendering index, or CRI, can be medium or high. It usually ranges from 60 to the 90s. This means you can see colors clearly for jobs that need true color.
Here is a table that compares halide lights and LED lights:
Feature | Halide Lights (Metal Halide) | LED Lights |
|---|---|---|
Color Temperature Range | Up to 5500K | 2200K to 6000K |
Lumen Output Longevity | Drops quickly over time | Stays high for longer |
Ultraviolet/Infrared Radiation | Gives off both | Does not give off either |
CRI Range | Medium (60) to high (90s) | Wide (65 - 95) |
The color and brightness of the lamp depend on a few things. The temperature inside the arc tube is very important. Higher temperatures help the lamp make more light. The mix of gases and the shape of the arc tube also matter. These things help the lamp shine bright and show colors well.
Note: The lamp gives the best color and brightness when it is fully warmed up. The design and gas mix inside help keep the color steady.
Benefits and Drawbacks
Efficiency and Light Output
Halide Lights give off strong, bright light. A 150W metal halide lamp can make up to 12,600 lumens. This is good for big places like gyms or warehouses. But, their luminous efficiency is not as high as other lights. You can see the difference in the table below:
Lighting Type | Luminous Efficiency (lumens/watt) |
|---|---|
Metal Halide | Less than 30 |
High Pressure Sodium | 100 to 190 |
LED | More than 50 |
LEDs make better light for your eyes. They do not waste much light because they shine in one direction. Metal halide lamps get dimmer as they get older. LEDs keep their brightness for a longer time.
Tip: If you want the most efficient lights, pick LEDs instead of metal halide lamps.
Cost and Maintenance
You should think about the price to buy and keep your lights working. When you put in halide lighting, you pay for fixtures and bulbs. Every year, you pay for energy. For example, 30 fixtures can cost $2,349.00 for energy, or $78.30 for each fixture. Metal halide systems lose half their brightness halfway through their life. This means you need to change bulbs more often.
Lighting Type | Maintenance Requirement | Frequency of Replacement |
|---|---|---|
Metal Halide | Needs 'Group Re-Lamping' at 40% of rated life. | Every 1 to 2 years |
LED | Almost no maintenance because they last a long time (50,000 to 100,000 hours). | Replace less often |
LEDs cost more at first, but you save money later. You do not need to replace them as much and they use less energy.
Environmental Impact
Halide Lights have mercury inside, which is poisonous. If a lamp breaks, mercury vapor can get out and hurt people. Mercury can also get into rivers and lakes. It becomes more dangerous and builds up in fish. Because of this, you must recycle these lamps at special places. In the United States, the EPA Universal Waste Rule tells you how to handle and throw away mercury lamps. In Europe, the WEEE Directive says you must recycle them the right way.
Note: Do not put metal halide lamps in regular trash. Always recycle them to help the environment.
Technical Specs
Lumens per Watt
You can measure how much light a lamp gives by looking at its lumens per watt. This number tells you how much light you get for each unit of energy. Metal halide lamps usually give you between 60 and 100 lumens per watt. This is good, but not the best. LED lights can give you even more, from 100 to 150 lumens per watt. You can see the difference in the table below:
Lighting Technology | Lumens per Watt |
|---|---|
Metal Halide | 60–100 |
LED | 100–150 |
Over time, halide lights lose brightness. When you first use a new lamp, you might see up to 36,000 lumens. After six months, you can lose about 20% of that light. If you use the lamp for 10,000 hours, you might only get half the original brightness. This drop in light is called lumen depreciation.
Time Period | Lumen Output Loss |
|---|---|
Initial (0 months) | 36,000 lumens |
After 6 months | 20% loss |
After 10,000 hours | 50% of initial output |
Tip: You should plan to replace halide lamps before they get too dim.
Lifespan
You can expect metal halide lamps to last for a set number of hours. The average lifespan is the time when half of the lamps still work. Most metal halide lamps are tested with a burn cycle of at least 10 hours per start. This helps you know what to expect in real life.
Many things can change how long your lamp lasts:
Quality of the ballast: A good ballast keeps the lamp running smoothly.
Temperature conditions: Very hot or cold places can shorten lamp life.
Frequency of switching: Turning the lamp on and off often can wear it out faster.
Maintenance practices: Cleaning and checking connections helps your lamp last longer.
Note: You can make your lamps last longer by using them in the right way and keeping them clean.
Color Rendering
You want your lights to show colors clearly. The Color Rendering Index (CRI) tells you how well a light shows true colors. Scientists measure CRI by shining the lamp on eight special colors and comparing the results to sunlight. Metal halide lamps can have a CRI from 17 up to 96, depending on the type. Most commercial halide lamps have a CRI between 60 and 90. This means you can see colors well, but not as perfectly as with sunlight or halogen lamps.
Light Source Type | Typical CRI Values |
|---|---|
Incandescent/Halogen Lamps | 100 |
Gas Discharge Lamps | 17 to 96 |
LEDs | 60 to 99 |
Tip: If you need to see colors very clearly, look for lamps with a higher CRI.
Applications of Halide Lights

Commercial and Industrial Use
Halide Lights are used in many big places. You see them in stores, sports arenas, and outside areas. They are in mobile light towers at building sites and in factories. These lights are very bright, so you need fewer of them. They help you see colors clearly and make things look real. Halide Lights last a long time, usually 10,000 to 15,000 hours. You do not have to change bulbs often. They also use energy well, so you save money.
Tip: Halide Lights help keep work areas safe. They give steady light and color. This helps you see small things and avoid getting hurt.
Here is a table that shows how much metal halide lights are used in different places:
Application Sector | Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
Mobile Lighting Equipment | 15–17 |
Outdoor Lighting | 8–9 |
Construction Equipment | 5–6 |
Industrial Lighting | 4–5 |
Temporary Lighting | 3–4 |
Horticulture and Sports
Halide Lights help plants grow inside. They also light up sports fields. Plants need bright light to grow strong. Stadiums and arenas use these lights because they are very bright. This makes it easy to watch games. These lights take 5 to 10 minutes to get bright. They can last up to 20,000 hours, but you might need to change them sooner than LEDs. They use more power and can get hot, so you need to cool them. If the power goes out, you have to wait for the lights to turn back on.
Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
High Brightness | Lights up large sports venues and plant rooms |
Warm-Up Time | Needs 5–10 minutes to reach full brightness |
Lifespan | Lasts 10,000–20,000 hours |
Energy Consumption | Uses more power than LED |
Sensitivity to Power Interruptions | Takes time to restart after power loss |
Evolution and Variations
Halide Lights have changed over time. In the 1960s and 1970s, people wanted better lights. They wanted lights that used less energy and showed colors better. In the 1980s and 1990s, new ceramic arc tubes made the lights last longer. In the 2000s, pulse-start designs helped save more energy. In the 2010s, makers used less mercury and made the lights better for the earth. Today, you still see metal halide lamps in special places, even though LEDs are more popular.
Here is a list that shows how Halide Lights have changed:
1960s–1970s: Lights got better at saving energy and showing colors.
1980s–1990s: Ceramic arc tubes made lights last longer.
2000s: Pulse-start designs helped save more energy.
2010s: Less mercury and better for the earth.
Present Day: Still used where strong, white light is needed.
You can pick from different kinds of halide and LED lights. The table below shows how they are different:
Feature | Metal Halide Lights | LED Lights |
|---|---|---|
Lifespan | 6,000–15,000 hours | 50,000–100,000 hours |
Efficiency | 3–5x incandescent bulbs | Highly efficient |
Color Temperature | Up to 5500K | High-quality light |
Warm-up Time | 15–20 minutes | Instant on |
Maintenance Costs | Higher | Low |
Light Direction | Omnidirectional | Directional |
Note: You might still use Halide Lights for their strong light and color. But LEDs last longer and cost less to use.
Halide lights make bright, white light for many places. They help you see colors well and use energy wisely. This is good for sports arenas, stores, and factories. These lights last a long time and save you money. Halide lights are still important because they work with smart systems and new technology. You see them in big spaces that need lots of light. As lighting changes, halide lights still give steady light and help people see clearly.
FAQ
What makes halide lights different from regular bulbs?
Halide lights use special gases and salts to create bright, white light. You get better color and more light than with regular bulbs. These lights work well in big spaces like gyms and stores.
How long do halide lights last?
You can expect halide lights to last between 10,000 and 20,000 hours. If you use them every day, you might need to replace them after a few years. Good care helps them last longer.
Are halide lights safe for the environment?
You must recycle halide lights because they contain mercury. Mercury can harm people and animals. Always take old lamps to a recycling center. Never throw them in the trash.
Where should you use halide lights?
Place | Why Use Halide Lights? |
|---|---|
Sports arenas | Bright, even lighting |
Stores | True color for products |
Factories | Strong light for safety |
Plant rooms | Helps plants grow indoors |
Can you replace halide lights with LEDs?
You can switch to LEDs for better efficiency and longer life. LEDs use less energy and need less maintenance. You save money over time and help the environment.
See Also
Exploring LED High Bay Lights: Uses, Advantages, and Choosing Tips
Understanding LED Industrial High Bay Lights: Uses, Benefits, and Setup Guidelines
LED Light Bulbs: Innovations, Advantages, and Choosing Advice
LED Indoor Lighting Solutions: Efficiency, Varieties, and Modern Uses
GE LED Bulbs: Characteristics, Advantages, and How to Choose

